Alzheimer’s: A mystery of memory loss…
Introduction
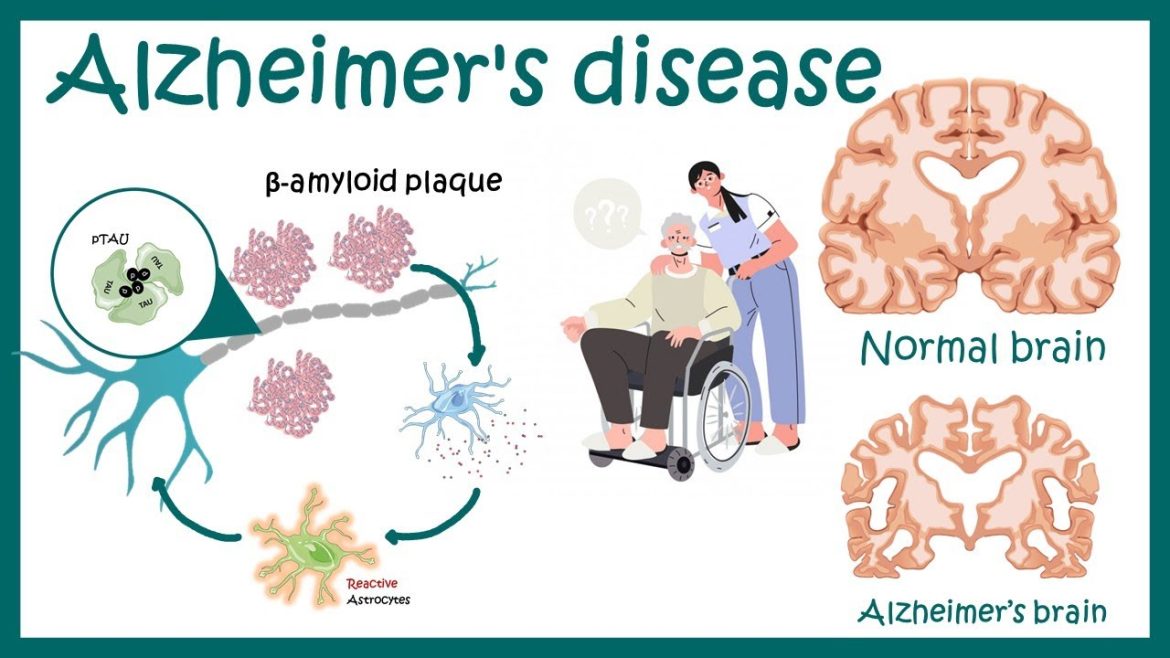
When it comes to dementia, Alzheimer’s disease is by far the most prevalent and devastating form. Memory, reasoning, and language are just some of the cognitive abilities that deteriorate over time in those with dementia. Alterations in temperament and conduct are also possible as the disease advances. It is estimated that millions of people worldwide suffer from Alzheimer’s disease, for which there is currently no treatment. The severity of symptoms can be lessened and the disease can be better managed with early diagnosis and treatment.
Managing the Emotional Impact of an Alzheimer’s Diagnosis
It’s natural to feel anxious, scared, or unsure of the future after receiving a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Although Alzheimer’s disease is a degenerative and ultimately fatal disease, it is important to remember that there are strategies for dealing with the diagnosis and mitigating its symptoms.
A thorough familiarity with the illness and its effects is the first step. Learn as much as you can about Alzheimer’s disease and the treatments available, and consult your doctor for further direction. If you have a better grasp of the disease and its treatment options, you’ll feel more confident and in charge of your life.
As a corollary, it is crucial to keep in touch with people and develop a solid network of resources. If you or a loved one are dealing with Alzheimer’s disease, it may help to join a support group where you can share your experiences, learn from others, and feel understood.
Take care of your physical wellbeing, as the third piece of advice. Getting regular exercise is a great way to improve your stamina, focus, and health. Be sure you’re getting enough rest and taking your medication as directed.
Last but not least, remember to pamper yourself and indulge in your passions every once in a while. Find a way to relax, whether that’s reading, taking a stroll, or just sitting back and listening to music. If you want to keep your brain from atrophying, it’s a good idea to engage in some form of mental exercise every day, like doing crossword puzzles or playing board games with loved ones.
Understanding the disease, surrounding yourself with caring people, prioritizing your physical health, and making time for yourself are all ways to help you manage the challenges of Alzheimer’s disease.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease’s Progression
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a degenerative brain disease that causes cognitive decline and eventually dementia. Dementia, the umbrella term for memory loss and other cognitive abilities severe enough to interfere with daily life, has Alzheimer’s disease as its most common cause. Over 5 million Americans are thought to be living with Alzheimer’s, a progressive neurodegenerative disease.
Commonly, the Alzheimer’s disease progression is categorized as mild, moderate, or severe. The symptoms experienced by those in each stage of the disease progression are distinct and may differ from one individual to the next.
The most common symptom in the early stage is temporary forgetfulness. A person may have trouble remembering recent conversations or events, or they may struggle to find the right word for a sentence. Mood and behavior shifts, such as increased confusion, apathy, and depression, are also possible at this stage.
Memory loss and confusion worsen during the moderate phase. A person may have trouble with regular activities such as paying bills or making phone calls, as well as forgetting familiar names and places. It’s also possible that he or she will have trouble communicating verbally, such as by stumbling over words.
A person with Alzheimer’s disease in the severe stage will become increasingly confused and will need help with most daily tasks. Also, personality shifts like increased anxiety or agitation are possible. When the disease progresses to its later stages, it can cause a person to need constant assistance with even the most basic of tasks.
It is currently unknown how to stop the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, and the disease itself cannot be reversed. However, the disease’s progression can be slowed and symptoms alleviated with the help of medication and other treatments. Anyone suffering from Alzheimer’s should have access to regular medical care and a support system in place. What You Need to Know About Nutrition and Alzheimer’s Disease/h1> Alzheimer’s disease is a degenerative brain disorder that progressively impairs one’s ability to remember, think, and perform even the most basic of tasks. As of the year 2020, it will rank as the sixth leading cause of death in America. Alzheimer’s disease can be prevented and treated in part through dietary changes.
The Alzheimer’s Association suggests a diet that is high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean proteins while being low in saturated fat, trans fat, cholesterol, salt, and added sugar. Getting enough of the vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that have been shown to reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease is essential.
Antioxidants are substances that can scavenge free radicals and prevent their harmful effects. Alzheimer’s disease has been linked to oxidative stress, which can be caused by free radicals. Protecting the brain from harm can be accomplished by eating foods high in antioxidants, such as blueberries, strawberries, spinach, and kale.
Omega-3 fatty acids, which can be found in abundance in fish, have been linked to a lower risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Inflammation in the brain is thought to contribute to the onset of Alzheimer’s disease, but new research suggests that omega-3 fatty acids may help alleviate this problem. A diet that includes fatty fish twice or thrice weekly, like salmon or mackerel, is highly recommended.
The B-complex vitamins (B6, B12, and folate) have protective effects against Alzheimer’s disease. You can get your B6 from foods like potatoes, bananas, and spinach, and your B12 from foods like meat, eggs, and dairy. Foods like dark green vegetables, beans, and fortified cereals are good sources of folate.
The risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease can be lowered by making dietary and other lifestyle changes, among other things. Some examples are going for frequent walks, playing sports, reading, playing games, and spending time with friends and family.
Alzheimer’s disease is best prevented and treated when nutrition is prioritized. The most important thing is to eat a healthy, well-rounded diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean proteins while being low in saturated fat, trans fat, cholesterol, salt, and added sugar. Be sure to get sufficient amounts of antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins B6, B12, and folate in your diet as well. Finally, take part in other lifestyle activities like working out frequently, getting enough sleep, minimizing stress, and enjoying activities like reading, playing games, and interacting with friends and family.
Tips for Caring for an Alzheimer’s Patient
The person with Alzheimer’s disease and their loved ones go through a challenging time every day. Problems adapting to the disease’s effects on behavior and cognition often arise as the illness worsens. Providing emotional support to a loved one with Alzheimer’s disease requires patience, understanding, and a willingness to accept the person as they are.
A thorough understanding of Alzheimer’s disease is the first step in helping a person who is dealing with it. You will be better able to detect changes as they occur and adapt to them if you are familiar with the course of the illness and the symptoms that accompany it. It can also be helpful to learn about local support groups and other resources in your area.
The next thing to do is make sure everyone is safe and content. They can feel safer in their own home if it is well-organized and simple to get around in for the person with Alzheimer’s. Furthermore, it can be useful to create simple reminders, such as post-it notes or labels for commonly used items around the house.
Emotional support is equally crucial. The smallest gestures, like showing your loved one you’re listening and care, can go a long way toward easing their mind and heart. Recognize their emotions and keep treating them with dignity and appreciation. It could also help to put them in touch with others who can relate to their situation.
Remember to take care of yourself at the end. The emotional and physical demands of caring for an Alzheimer’s patient can be substantial. You can refuel your patience and tolerance with time spent sleeping, working out, and socializing with loved ones.
The rewards of helping a loved one through Alzheimer’s disease can far outweigh the difficulties. Helping a loved one cope with a disease requires patience and understanding on your part, as well as self-care and education.
Conclusion
Millions of people around the world are living with Alzheimer’s disease, a chronic neurodegenerative condition that progressively worsens their quality of life. Memory loss and mental decline are hallmarks of this disease, which can ultimately result in total helplessness. There may not be a way to stop the progression of Alzheimer’s disease just yet, but there are treatments and therapies that can help. The progress made in the study of Alzheimer’s disease and its potential treatments gives rise to optimism that a cure will be discovered.