Genetically modified organisms, or GMOs, refer to living organisms that have been genetically modified using biotechnology techniques. These techniques allow for the insertion, deletion, or modification of specific genes within the organism’s genome.
There are several techniques used in genetic modification, including:
Gene insertion: This involves inserting a gene from one organism into the genome of another organism. This can be done using a vector, such as a virus or plasmid, to carry the gene into the target organism.
Gene deletion: This involves removing a gene from an organism’s genome. This can be done using techniques such as CRISPR-Cas9, which uses a specific enzyme to cut out a specific piece of DNA.
Gene editing: This involves making specific changes to the DNA sequence of an organism. This can be done using techniques such as CRISPR-Cas9, which allows for precise editing of the genome.
Gene silencing: This involves reducing the expression of a specific gene without changing its DNA sequence. This can be done using techniques such as RNA interference, which uses small RNA molecules to inhibit the expression of a specific gene.
These techniques allow for the precise manipulation of an organism’s genome, enabling the creation of genetically modified organisms with specific traits.
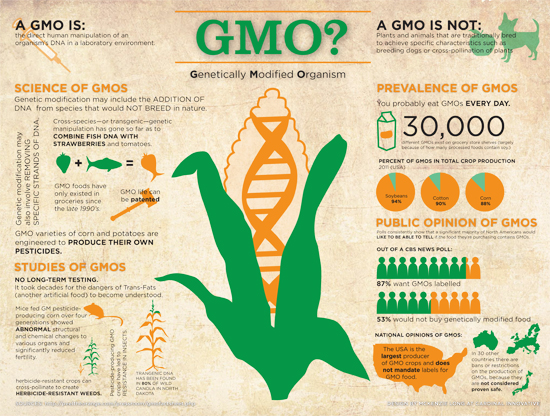
The use of GMOs in agriculture has increased significantly in recent years, with genetically modified crops such as corn, soybeans, and cotton being widely grown around the world. These crops have been modified to be resistant to pests and diseases, and to improve their yield and nutritional content.
Some examples of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) include:
Bt corn: This type of corn has been genetically modified to produce a protein from the Bacillus thuringiensis bacteria, which is toxic to certain insects. This makes the corn resistant to pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
Roundup ready soybeans: These soybeans have been genetically modified to be resistant to the herbicide Roundup, allowing farmers to use the herbicide to control weeds without damaging the soybeans.
Golden rice: This type of rice has been genetically modified to produce beta-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A. This helps to address vitamin A deficiency, a major cause of blindness and other health problems in developing countries.
Insect-resistant cotton: This type of cotton has been genetically modified to produce a protein from the Bacillus thuringiensis bacteria, which is toxic to certain insects. This makes the cotton resistant to pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
These are just a few examples of the many GMOs that have been developed. Others include genetically modified tomatoes, potatoes, and strawberries, among others.
One of the main benefits of GMOs is that they can help to increase crop productivity and reduce the need for chemical pesticides and herbicides. This can lead to higher yields and lower costs for farmers, as well as better food security for consumers.
One of the main uses of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in agriculture is to create crops that are resistant to herbicides. Herbicides are chemicals that are used to control weeds, and they can damage or kill crops if they are not carefully applied.
GMO crops that are resistant to herbicides are designed to tolerate the application of specific herbicides, allowing farmers to use these chemicals to control weeds without damaging the crops. This can save farmers time and money, as they do not have to carefully apply the herbicides around the crops.
However, the widespread use of herbicides on GMO crops has also raised concerns. Some people are worried that the overuse of herbicides could lead to the development of herbicide-resistant weeds, which could be difficult to control. This could reduce the effectiveness of herbicides and make it more difficult for farmers to control weeds.
Additionally, the use of herbicides on GMO crops has been linked to environmental concerns, such as the loss of biodiversity and the contamination of water sources. Some people are concerned that the widespread use of herbicides on GMO crops could have negative impacts on the environment.
Overall, the use of GMO crops that are resistant to herbicides can provide benefits for farmers, but it is important to carefully consider the potential risks and environmental impacts.
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a bacterium that produces proteins that are toxic to certain insects. These proteins are used as a natural insecticide, and they have been used in agriculture for many years.
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) that are resistant to Bt toxins are created by inserting a gene from the Bt bacteria into the genome of the target organism. This gene codes for the production of the Bt toxin, which is toxic to insects that feed on the GMO crop.
The use of Bt toxins in GMOs has several advantages. First, Bt toxins are a natural insecticide, so they are less harmful to humans and the environment compared to chemical insecticides. Second, Bt toxins are specific to certain insects, so they do not harm beneficial insects or other organisms.
However, the widespread use of Bt toxins in GMOs has also raised concerns. Some people are worried that the overuse of Bt toxins could lead to the development of Bt-resistant insects, which could be difficult to control. This could reduce the effectiveness of Bt toxins and make it more difficult for farmers to control pests.
Additionally, the use of Bt toxins in GMOs has been linked to environmental concerns, such as the loss of biodiversity and the contamination of water sources. Some people are concerned that the widespread use of Bt toxins in GMOs could have negative impacts on the environment.
Overall, the use of GMO crops that are resistant to Bt toxins can provide benefits for farmers, but it is important to carefully consider the potential risks and environmental impacts.
However, the use of GMOs has also sparked a debate about their safety and environmental impacts. Some people are concerned that genetically modified crops may pose risks to human health, and that they could have negative effects on the environment, such as reducing the diversity of plants and animals in an ecosystem.
Despite these concerns, the majority of scientific research suggests that GMOs are safe for human consumption and the environment. Many regulatory agencies, such as the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), have extensively reviewed the safety of GMOs and have concluded that they are safe for use.
The use of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in agriculture has sparked a debate about their safety and potential risks. While the majority of scientific research suggests that GMOs are safe for human consumption and the environment, there are still some concerns about their potential dangers.
One potential danger of GMOs is that they could have negative effects on human health. Some people are concerned that eating genetically modified foods could lead to health problems, such as allergies, toxicity, or other negative effects. However, the majority of scientific research has not found any evidence of negative health effects from eating GMOs.
Another potential danger of GMOs is that they could have negative impacts on the environment. Some people are concerned that genetically modified crops could reduce the diversity of plants and animals in an ecosystem, and could lead to the contamination of non-GMO crops. However, there is no clear evidence that GMOs have negative impacts on the environment.
Additionally, the use of GMOs in agriculture has also raised concerns about their economic impacts. Some people are worried that the use of GMOs could lead to the concentration of power and control in the hands of a few large corporations, which could have negative impacts on farmers and consumers.
Overall, the potential dangers of GMOs are still the subject of debate and further research is needed to fully understand their risks and potential impacts.
Ultimately, the decision to use GMOs in agriculture should be based on a careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks. While there are valid concerns about their safety and environmental impacts, the use of GMOs can also provide many important benefits for farmers and consumers.